How to Transfer Files (Local and Remote) in Linux
Transferring files in Linux is something every system admin should know, especially when working across networks.
Two popular tools for this are SCP and Rsync. Both let you securely move files between local and remote systems with ease.
In this guide, we’ll go over how to use SCP and Rsync for file transfers, whether you’re working locally or across different machines.
scp (Secure Copy Protocol) in Linux
The scp command lets you securely copy files and folders between two computers over SSH. This means your data stays encrypted while transferring over the internet.
Here’s the basic syntax:
# scp [options] source_file destinationsource_file: The file or folder you want to copy.
destination: Where you want to copy it.
Copying Files Locally in Linux
To copy a file between folders on the same machine, use:
# scp file.txt /scp_folder/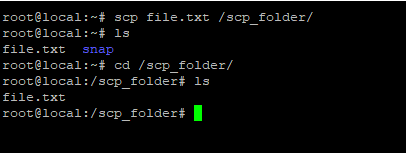
Copying Files to a Remote Server
To copy files from your computer to a remote server, just specify the server’s IP address and where you want the files to go.
# scp file.txt root@192.168.1.5:/root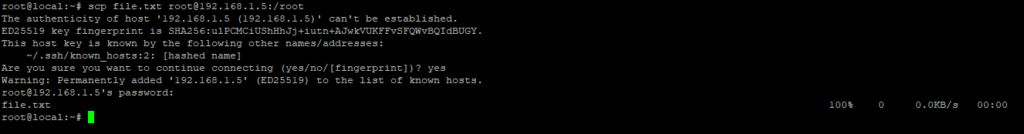
Copying Files from a Remote Server
To copy a file from a remote server to your local machine, just swap the source and destination.
# scp root@192.168.1.5:/root/bitscentric.txt /root
To copy a whole folder, use the -r option (short for recursive).
# scp -r dir/ /scp_folder/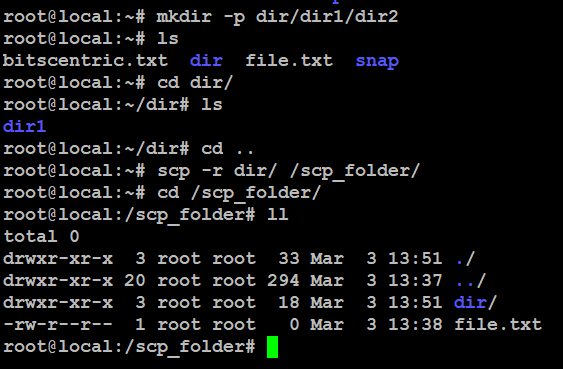
rsync in Linux
The rsync command is a popular tool for copying and syncing files between locations, often used to keep directories up to date.
The basic syntax for rsync is:
# rsync [options] source destinationTransfer Files Locally
To copy files or folders on your computer, use rsync -a to keep permissions, ownership, and timestamps intact. Add -v if you want to see the progress while it copies.
# rsync -av dir /backup/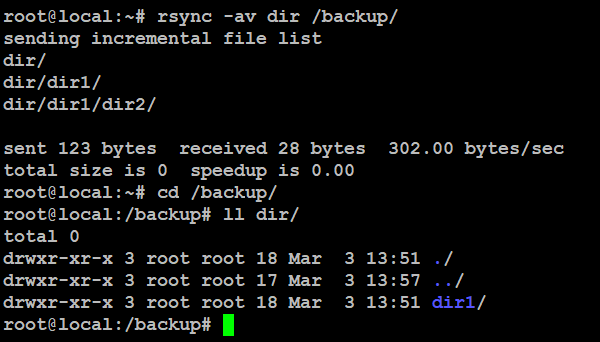
Transfer Files to a Remote Server
By default, rsync uses SSH to transfer files. Just specify the remote server’s IP and destination folder.
# rsync -av dir root@192.168.1.5:/root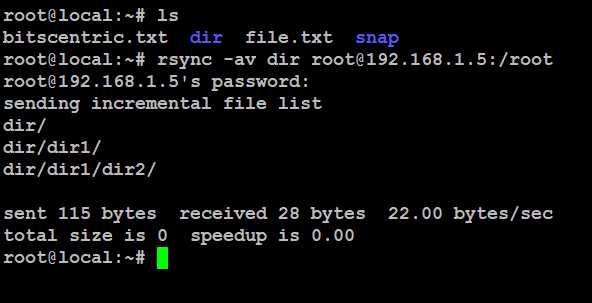
Note:- The command transfers “dir” to the remote server, and if you run it again, only the changed files will be copied.
Transfer Files from a Remote Server
To transfer files from a remote server to your local machine.
# rsync -av root@192.168.1.5:/root/bitscentric /root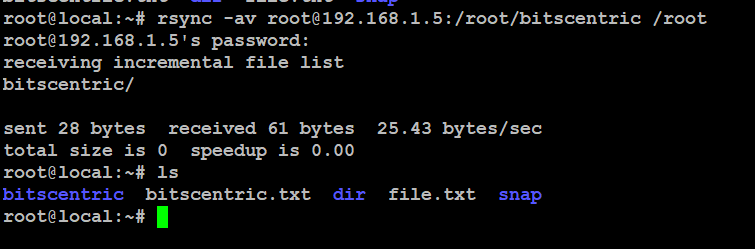
Synchronizing Directories with Rsync
Rsync is great at keeping two directories in sync, whether on the same computer or across different machines.
# rsync -av /root/folder/ root@192.168.1.5:/root/folder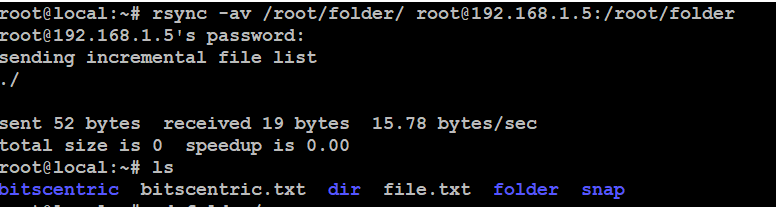
To sync a remote directory with your local one, just swap the source and destination in the rsync command.
# rsync -av root@192.168.1.5:/root/folder /root/folder/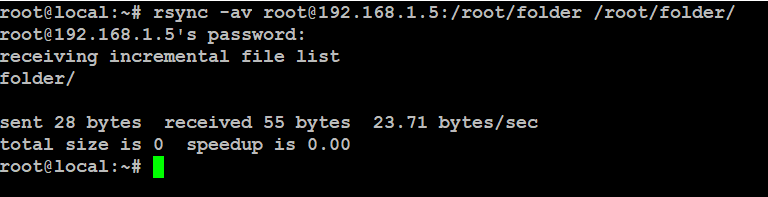
Note:- If a transfer gets interrupted due to a network issue or any other reason, you can pick up where it left off using the --partial option.
# rsync -av --partial /root/folder/ root@192.168.1.5:/root/folder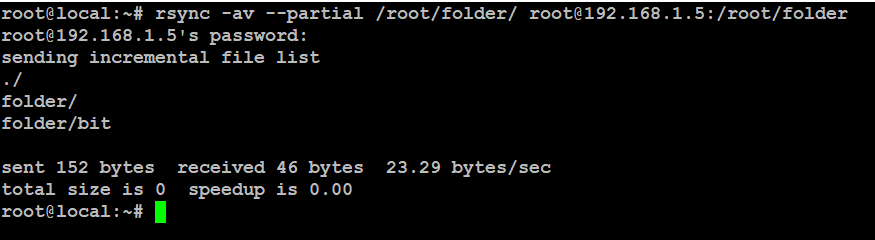
Transferring files in Linux is easy with tools like scp and rsync. scp is simple and secure, while rsync is great for syncing files efficiently. Knowing how to use them can make file management smoother across local and remote systems.
