How to List, Display, & View all Current Cron Jobs in Linux
Cron is a Linux tool that automatically runs scheduled tasks, like backups and updates, so you don’t have to do them manually.
Check Cron Jobs in Linux
Cron jobs are stored in special directories called crontabs, but their exact location depends on the Linux distribution.
On Ubuntu, user-specific cron jobs are kept in /var/spool/cron/crontabs, while system-wide jobs for the root user are found in /etc/crontab.
To see the system-wide cron jobs, open /etc/crontab with a text editor or use commands like cat, more, or less.
# cat /etc/crontab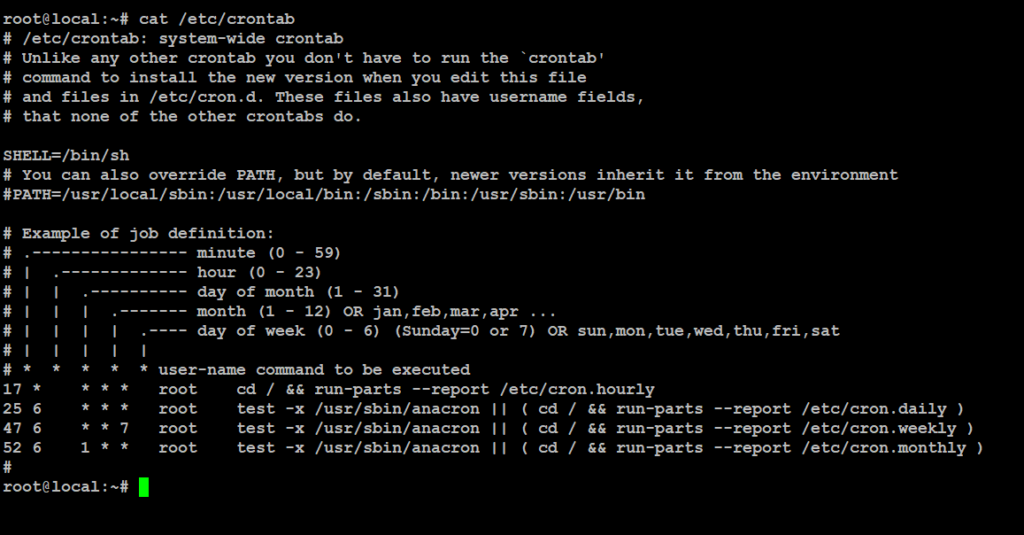
List All Active Cron Jobs
As a system administrator, it’s important to know how to check active cron jobs. The simplest way to see all scheduled cron jobs for your user is by running:
# crontab -l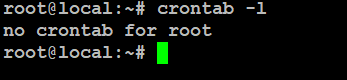
If you have any scheduled cron jobs, they’ll be listed. If not, you’ll see a message saying there are none. It also shows all cron jobs created by the root user.
View Cron Jobs by User
Checking user-specific cron jobs helps you keep an eye on scheduled tasks, spot issues, and catch any misconfigurations. It also helps you detect unauthorized jobs, making sure only approved tasks are running. This reduces security risks.
To see the cron jobs for a specific user, use:
# crontab -u root -l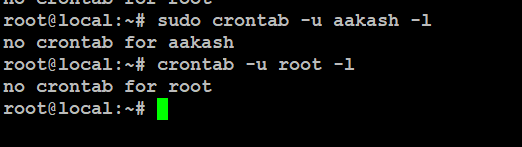
List Hourly Cron Jobs
Hourly cron jobs help automate tasks regularly, keeping things running smoothly and efficiently. To see a list of hourly cron jobs, use this command:
# ls -la /etc/cron.hourly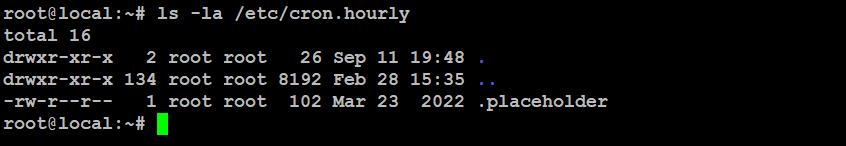
List Daily Cron Jobs
Daily cron jobs take care of important tasks like backups, log cleanup, and generating reports. To see the daily scheduled jobs, use this command:
# ls -la /etc/cron.daily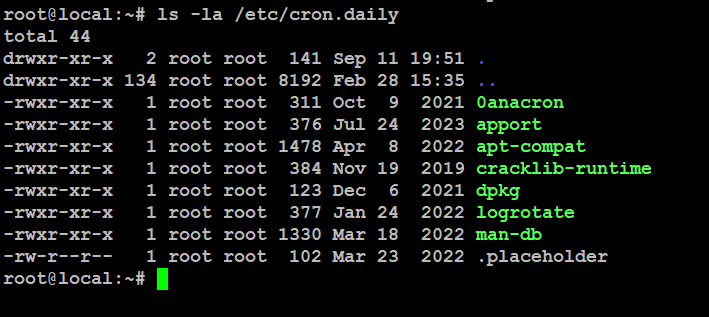
List Weekly Cron Jobs
Weekly cron jobs help automate tasks that need to run every week, like a full system backup every Sunday night. To see your weekly cron jobs, run this command:
# ls -la /etc/cron.weekly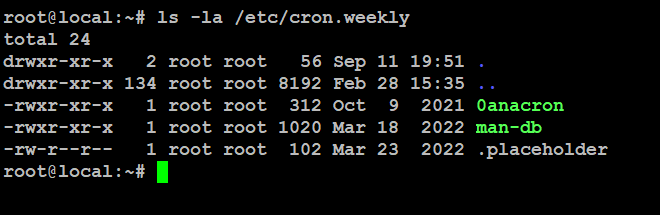
List Monthly Cron Jobs
Monthly cron jobs are great for automating tasks that run once a month, like system backups, report generation, or database maintenance. To see your monthly cron jobs, use this command:
# ls -la /etc/cron.monthly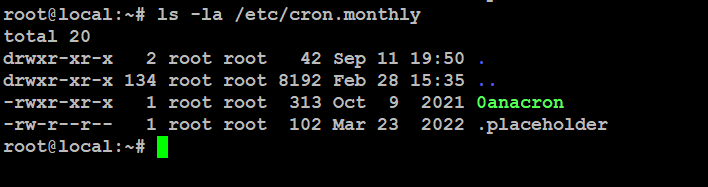
View Software-Specific Cron Jobs
Software-specific cron jobs are automated tasks set up to keep certain applications or services running smoothly. These tasks handle things like daily database backups, weekly log cleanups, monthly cache clearing, scheduled reports, and search indexing.
To check these software-related cron jobs, just take a look inside the cron.d directory.
# ls -l /etc/cron.d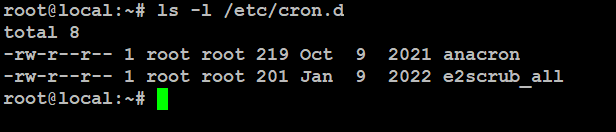
You can use the cat command or open the files in a text editor to check their contents and see the details of each scheduled cron job.
Now that you know how to view cron jobs on your machine, you can use this handy tool to schedule tasks, like running a job at startup. Follow the commands in this guide to sort and display scheduled tasks easily.
