How To Add Swap Space on Ubuntu 22.04
Swap is a section of your hard drive that acts like backup memory when your RAM is full. When your system runs out of RAM, it moves less-used data to the swap space. While this helps prevent crashes, it’s much slower than RAM, especially on non-SSD drives. Having swap space is a useful safety net to keep your system running smoothly during high memory usage.
Check Swap Status
Before we start, let’s check if there’s already some swap space available. A system can have multiple swap files or partitions, but usually, one is enough.
To check, run:
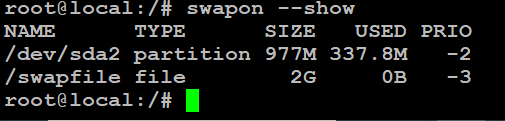
# swapon --show
If there’s no output, it means no swap space is active. You can also check with.
# free -h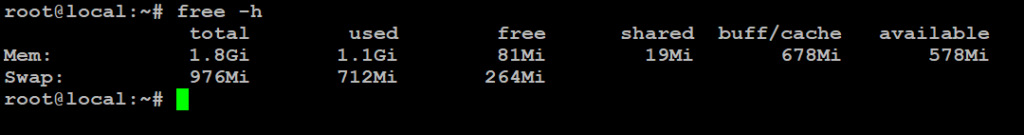
How to Increase Swap Size
Turn Off Current Swap
# swapoff -a
Resize the Swap File
# dd if=/dev/zero of=/swapfile bs=1M count=2048
bs=1M: Block size of 1MBcount=1024: 1024 blocks = 1GB
(Adjust the count to increase swap size. For 4GB, use count=4096.)
Set Correct Permissions
# chmod 600 /swapfileFormat as Swap
# mkswap /swapfile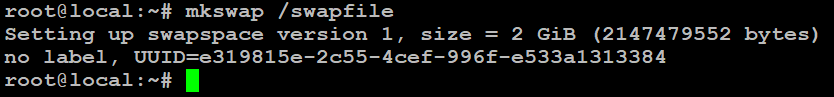
Enable the Swap
# swapon /swapfileVerify the Swap Size
# free -h
Make It Permanent
# vim /etc/fstab
/swapfile swap swap defaults 0 0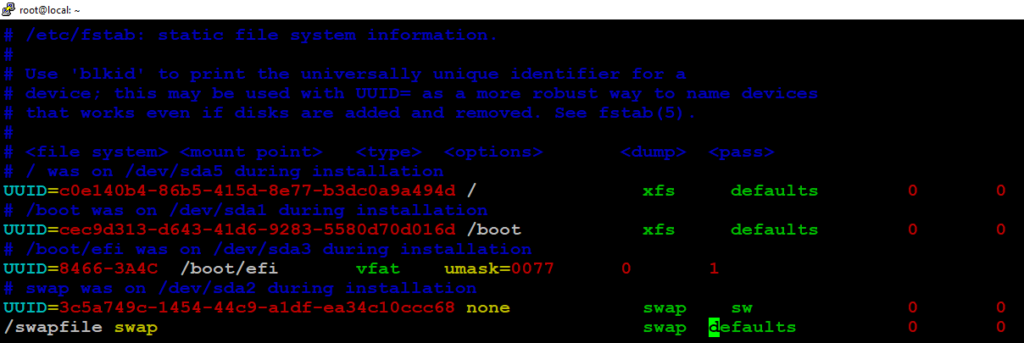
Verify that the swap is available
# swapon --show